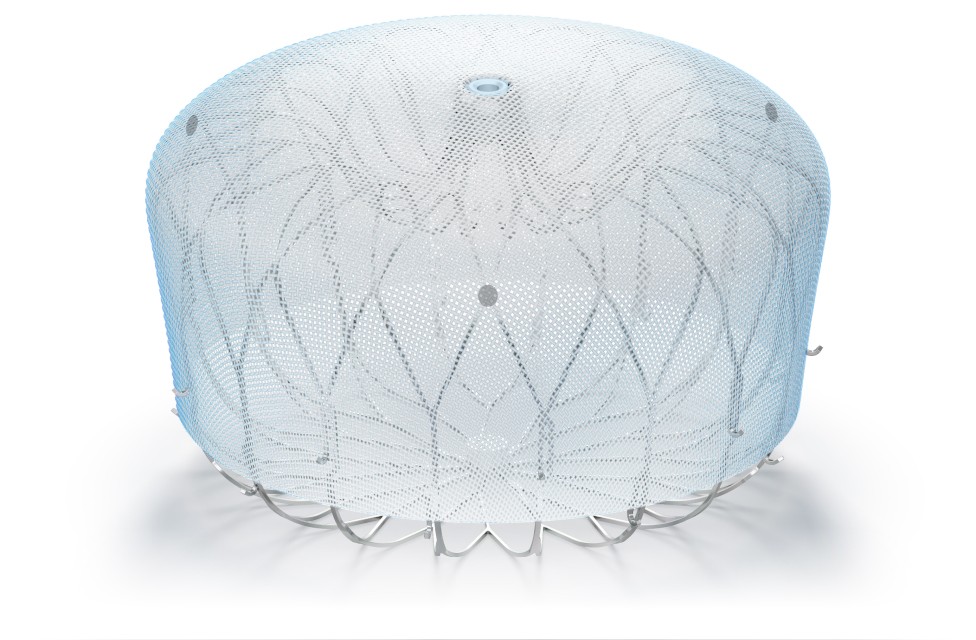
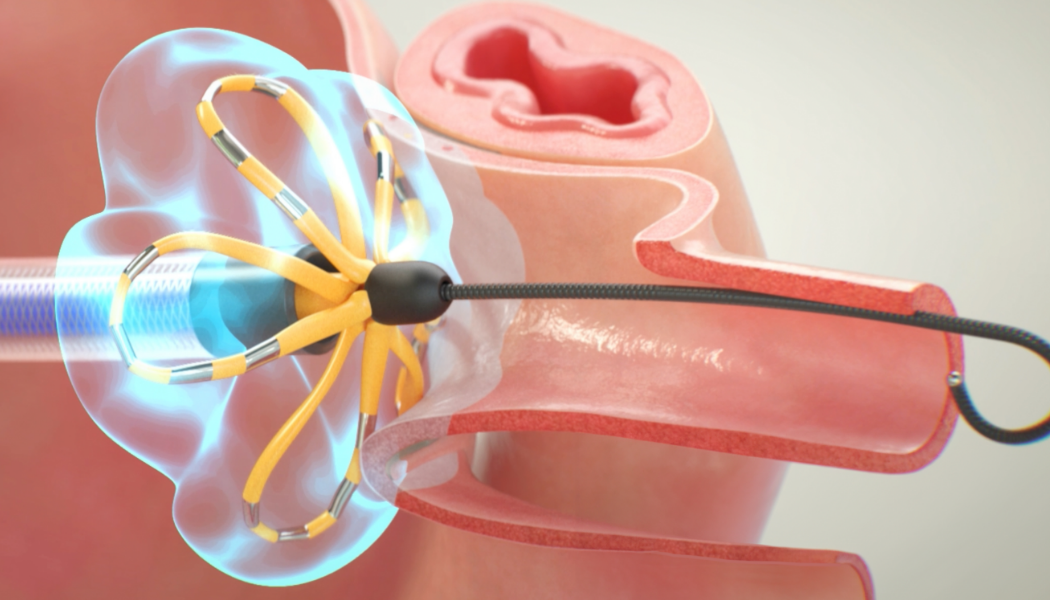
Note: The FARAPULSE PFA System is pictured as representative example for AFib ablation, though any modality may be used.
*In the OPTION trial, sequential LAAC was a minimum of 90 days (as a protocol-driven blanking period) and less than 6 months post-AF ablation.
†Thermal AFib ablation only.
References
1. Blackshear JL., Odell JA. Annals of Thoracic Surg. 1996; 61: 755-759.
2. FY25 IPPS Final Rule
3. Wazni O, et al. Randomized Comparison of Left Atrial Appendage Closure with Oral Anticoagulation After Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation. Late Breaking Clinical Trial, American Heart Association 2024.
4. Saliba W, et al. Comparison of Left Atrial Appendage Closure and Oral Anticoagulation after Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation Concomitant and Sequential Cohorts of the OPTION Randomized Controlled Trial. Late Breaking Clinical Trial, AF Symposium 2025
5. BSC data on file. 2025
6. Reddy VY, Gerstenfeld EP, et al; ADVENT Investigators. Pulsed Field or Conventional Thermal Ablation for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(18):1660-1671. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2307291.
7. Ekanem, E, Neuzil, P, Reichlin, T et al. Safety of pulsed field ablation in more than 17,000 patients with atrial fibrillation in the MANIFEST-17K study. Nat Med. 2024;30(7):2020-2029 doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-03114-3
8. Reddy VY, Mansour M, Calkins H. Pulsed Field vs Conventional Thermal Ablation for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: Recurrent Atrial Arrhythmia Burden. J Am Coll.Cardiol. 2024 Jul 2;84(1):61-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2024.05.001.
9. Reddy VY, Gerstenfield EP, Schmidt B, et al. Pulsed Field Ablation of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation With Continuous ECG Monitoring Follow-Up: ADVANTAGE AF-Phase 2. Circulation. Published online April 2025. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.125.074485
10. Della Rocca DG, Marcon L, Magnocavallo M, et al. Pulsed electric field, cryoballoon, and radiofrequency for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation ablation: A propensity scorematched comparison. Europace. 2023;26(1):euae016.
11. Füting A, Neven K, Howel D et al. Patient discomfort following pulsed field ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation – an assessment of chest and groin pain using the Numeric Rating Scale. Clin Res Cardiol (2021). 10.1007/s00392-021-01933-9
12. FARAPULSE Clinical Compendium