A One-Time Procedure.
A Life-Changing Alternative
"It was the best feeling to know that WATCHMAN was going to watch over me"
Marjorie Giovannoni, WATCHMAN recipient
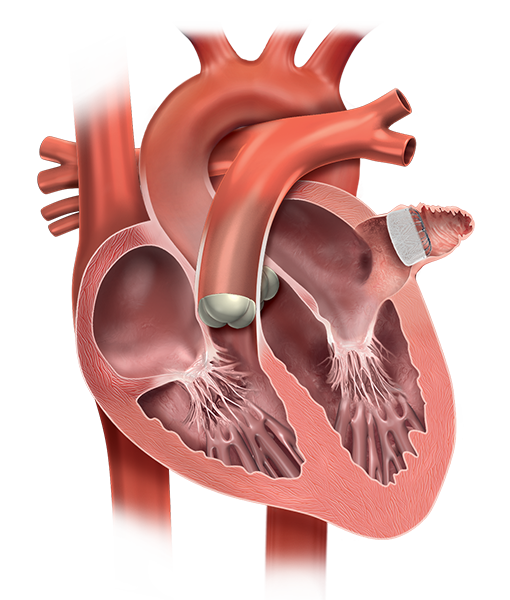
How WATCHMAN FLX Works
To understand how WATCHMAN FLX works, it helps to know more about the connection between atrial fibrillation and stroke.
Atrial fibrillation, or AF, affects your heart’s ability to pump blood normally. This can cause blood to pool in an area of the heart called the left atrial appendage, or LAA. There, blood cells can stick together and form a clot. When a blood clot escapes from the LAA and travels to another part of the body, it can cut off the blood supply to the brain, causing a stroke.2,3
WATCHMAN FLX is for people with atrial fibrillation not caused by a heart valve problem who need an alternative to oral anticoagulants. This website is intended to provide patients and caregivers with some information about the WATCHMAN FLX Implant. It may help prepare you for talking to your doctor about your options for reducing stroke risk.
Important Safety Information
The WATCHMAN and WATCHMAN FLX Devices are permanent implants designed to close the left atrial appendage in the heart in an effort to reduce the risk of stroke.
With all medical procedures there are risks associated with the implant procedure and the use of the device. The risks include but are not limited to accidental heart puncture, air embolism, allergic reaction, anemia, anesthesia risks, arrhythmias, AV (Arteriovenous) fistula, bleeding or throat pain from the TEE (Trans Esophageal Echo) probe, blood clot or air bubbles in the lungs or other organs, bruising at the catheter insertion site, clot formation on the WATCHMAN™ and WATCHMAN FLX Closure Devices, cranial bleed, excessive bleeding, gastrointestinal bleeding, groin puncture bleed, hypotension, infection/pneumonia, pneumothorax, pulmonary edema, pulmonary vein obstruction, renal failure, stroke, thrombosis and transient ischemic attack. In rare cases death can occur.
Be sure to talk with your doctor so that you thoroughly understand all of the risks and benefits associated with the implantation of the WATCHMAN and WATCHMAN FLX Devices.
CAUTION: The law restricts these devices to sale by or on the order of a physician. Indications, contraindications, warnings and instructions for use can be found in the product labeling supplied with each device. Information for the use only in countries with applicable health authority product registrations.
Content of this website is for Information Purposes only and not meant for product promotion or medical diagnostic. This information does not constitute medical or legal advice, and Boston Scientific makes no representation or warranty regarding this information or its completeness, accuracy or timeliness.
Accordingly, Boston Scientific strongly recommends that you consult with your physician on all matters pertaining to your health or to address any questions.
References
- Holmes DR Jr, Kar S, Price MJ, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64(1):1-12.
- Blackshear JL, Odell JA. Appendage obliteration to reduce stroke in cardiac surgical patients with atrial fibrillation. Ann Thorac Surg. 1996;61:755-759.
- National Stroke Association. Making the Afib-Stroke Connection. https://www.stroke.org/sites/default/files/resources/Afib-Connection%20for%20hcp.pdf. Published 2012. Accessed September 1, 2016.
- Holmes DR Jr, Doshi SK, Kar S, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65(24):2614-2623.